If you are looking to understand the range of the bass guitar, you are on the right track as a musician.
I say this because knowing the instrument`s range is crucial for understanding the role of the bass. It will also help you in writing basslines that work well with the other instruments in a band. But first things first, what is the range of a bass guitar?
A 4-string bass guitar tuned to E standard has a range of E1-D#4 with 20 frets and E1-G4 with 24 frets. 5-string basses have a range of B1-E4 with 21 frets, while 6-string basses have a range of B1-A4.
However, there is a lot more that goes into understanding the range of a bass guitar. Therefore, I`ve written this short guide to show you everything you need to know about the subject.
I`ll start by covering how much melodic range the instrument has, and showcase this on a treble clef. Then, I`ll cover the frequency range of the bass guitar. For this, I`ve made a graph that compares the frequency range of the 4, 5, and 6-string bass against the guitar.
Lastly, we will take a look at how to change the range of a bass, and how low it can be tuned. With this information, you will gain a deeper understanding of the instrument, which will expand your versatility as a musician and composer.
Bass guitar range on a staff
Using sheet music to understand the range of the bass is not as straightforward as it might seem.
Before I show you why here is what the range of a 4-string bass looks like on the bass clef. This assumes the bass is tuned to E standard and has 21 frets, which results in exactly 3 octaves of total range.
Note: Basses generally have between 20 and 24 frets. Thus, some basses will have slightly more, while others will have lightly less range than this.
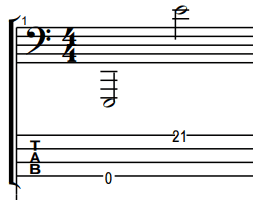
Here is what the high E looks like on the treble clef:
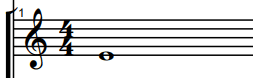
However, as I showcased in my article about Middle C on the bass guitar, the bass is a transposing instrument. This means that in notation, the bass is written differently from how it actually sounds.
Specifically, the bass is written an octave higher than it is played.
Playing the open E string results in a pitch of E1. However, for the sake of convenience, this is written out as an E2 in sheet music.
This ultimately makes sheet music a lot easier to read. If we were to write bass notation untransposed, we would constantly stray way below the bass clef and need lots of extra lines.
For this reason, this is what the full transposed range of the bass looks like on the bass clef:
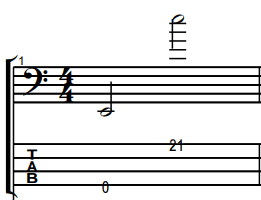
And here is where the high E would be notated on the treble clef:
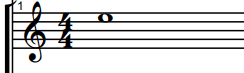
Bass guitar frequency range
A 4-string bass guitar with 21 frets has a frequency range of 41.2Hz to 329.63Hz when tuned to E standard. A 5-string Bass tuned to B standard has a frequency range of 30.87Hz to 329.63Hz if it has 21 frets.
Thus, 4-string basses with 21 frets have exactly 3 octaves of range. This range can be further extended by utilizing a drop tuning and tuning down the lowest string of the instrument.
A 5-string bass with 24 frets is two whole notes shy of having 4 octaves of range. 6-string basses have 4 full octaves of range if they have 23 frets or more.
To get a better feel for the difference between the frequency range of the instruments I made a chart. I also added the frequency range of an electric guitar, to showcase how much basses of all types differ from it:

The 4-string bass is tuned exactly an octave below the guitar. The 5 and 6-string bass are tuned an octave and a perfect fourth below it. As the guitar has 6 strings and frequency ranges increase exponentially at higher pitches, it has a significantly wider frequency range than the bass.
It`s also worth mentioning that the bass can, and will, produce frequencies that are higher than in the graph above.
These sounds are called harmonic partials. When you play any note on the bass guitar, harmonic partials will ring out in addition to the note you are playing. In general, these are significantly lower in volume than the note that is being fretted.
As a result, harmonic partials are hard to notice unless your bass has an intonation issue, or your ears have excellent pitch.
What is the lowest note a bass guitar can play?
In E standard, the lowest note a 4-string bass can play is E1. 5-string basses are commonly tuned to B standard, and their lowest note is a B0. Bass guitars can be tuned down to reach even lower notes, and have been tuned down to reach notes as low as A-1.
In their respective standard tunings, here`s what the lowest note on 4 and 5-string basses look like on the bass clef. Keep in mind that they sound out an octave lower than this:

With that said, bass guitars can be tuned down to reach even lower notes. For example, in metal and rock, it is common to tune bass guitars to Drop D. For a 4-string bass this results in an additional whole note of deep range. As a result, its lowest note is a D1 instead of an E1.
Most bassists that tune their instruments down tend to not tune down past A Standard, which makes the lowest note an A0. This low A has a frequency of 27.5hz.
This is in part because past A Standard, the bass starts to sound excessively deep. As you also need significantly thicker strings and gear that can withstand the lower frequencies, utilizing tunings past this point can also be cumbersome.
However, when researching how low a bass guitar can be tuned, I found that some bands have played as low as Double Drop A. In the case of Double Drop A, this results in the lowest note of the bass becoming an A-1. This note has a frequency of 13.75Hz.
Some bands that play this low use octave pedals to pitch shift the bass instead of tuning it down. Despite this, this goes to show that basses can be tuned down to pitches that are not discernable to the human ear, but still work in the context of a band.
Conclusion
As you can tell by now, the bass guitar has a very limited range compared to instruments like the guitar and the piano. In return, the bass fills an important role in bands by filling in the low part of the frequency spectrum.
In other words, without bass bands would sound hollow. This is a major reason most bands have a bass player.
When writing bass lines for music, it is beneficial to keep these ranges in mind. This is because you want to ensure that the bass does not clash with the other instruments and that it fills in the low end.
In a band, it is best to make use of the low range of the bass to avoid playing in the same frequency range as the keyboard, or guitar. By doing this, your basslines will sound like a distinguishable part of the song. They will also work better with the other instruments of a band, and as a result, make them sound better.

